Radare2 framework Ultime Guide Part 1 Introduction
 In this suite of articles, we will learn how to use radare2 for effective reverse engineering.
In this suite of articles, we will learn how to use radare2 for effective reverse engineering.
So what is radare2 !?
created by Pancake, Radare2 is a reverse engineering powerful framework. It is cross plateform tools. This mean that you can use it on linux/windows/macOS/Android.
Inlike other reverse engineering tool like IDA, Binary ninja, radare2 is open source and the core of it is a command line tools.
It is a powerfull reverse engineering framework which come with a lot of subtools which we will overview in this tutorial part.
Radare2 is powerful tool but the learn curve of it can be long. It can take time and effort/pratice to become confortable with it. But believe me, when you will be familiary with this tool, you will get a lot of powerful in your reverse engineering carrer.
If you are CTF Player especially REV challenges, It will be very important for you to know Radare2. It will help you to solve crackmes durant CTF competition.
Radare2 is not only made for CTF players. It is made also for real live vulnerabilities researchers (Reverse engineers, bug hunters, and so on).
So if you plan to make reverse engineering or vulnerabilities researche (binary side) your carrer, it will be very important for you to master Radare2 skills.
This part will be a litte introduction of the tool.
in the next chapters, we will deep dive into the internal work of the tools and use it to solve reverse engineering challenge.
Hope you enjoy this serie
Radare2 INSTALLATION Radare2 framework toolchain
Radare2 framework core overview
Binary open modes Interfaces Radare2 commands overview
Radare2 INSTALLATION
You can install Radare2 in multiple way.
. By using apt if your are on debian based system
sudo apt install radare2
. By downloading the precompiled version for your machine.
you can found it on radare github page
. By cloning radare repo and install it manualy
git clone https://github.com/radareorg/radare2.git ; cd radare2 ; ./sys/install.sh | sys/install.bash
see radare2 github
Radare2 framework toolchain
Radare2 comes with a lot of utilities that help to perform reverse engineering tasks.
- radare2 the core compoment
It is the main compoment of radare2 framework. It include: - Disassembler
- Debugger
- static and dynamic analyse capability
- binary patching .. and other
radare2 snipped help
$radare2 -h
Usage: r2 [-ACdfjLMnNqStuvwzX] [-P patch] [-p prj] [-a arch] [-b bits] [-c cmd]
[-s addr] [-B baddr] [-m maddr] [-i script] [-e k=v] file|pid|-|--|=
-- run radare2 without opening any file
- same as 'r2 malloc://512'
= read file from stdin (use -i and -c to run cmds)
-= perform !=! command to run all commands remotely
-0 print \x00 after init and every command
-1 redirect stderr to stdout
-2 close stderr file descriptor (silent warning messages)
-a [arch] set asm.arch
-A run 'aaa' command to analyze all referenced code
-b [bits] set asm.bits
-B [baddr] set base address for PIE binaries
-c 'cmd..' execute radare command
-C file is host:port (alias for -c+=http://%s/cmd/)
-d debug the executable 'file' or running process 'pid'
-D [backend] enable debug mode (e cfg.debug=true)
-e k=v evaluate config var
-f block size = file size
-F [binplug] force to use that rbin plugin
-h, -hh show help message, -hh for long
-H ([var]) display variable
-i [file] run script file
-I [file] run script file before the file is opened
-j use json for -v, -L and maybe others
-k [OS/kern] set asm.os (linux, macos, w32, netbsd, ...)
-l [lib] load plugin file
-L, -LL list supported IO plugins (-LL list core plugins)
-m [addr] map file at given address (loadaddr)
-M do not demangle symbol names
- rabin2
rabin2is a binary static analyse tool that help to gather a lot of information on the binary you are about to reverse. Whith rabin2 , you can :
. Get the programming langage used to create the binary
. The compilers
. The architecture/machine on which the binary must be running
. The status of some security mitigation like PIE(Position Independence Execution), ASLR (Adress Space Layout Randomize)
. and others things.
Those informations is very helpful to success in your reverse.
It can help you to choice which tools to use to do the reverse. For example, if you found that the binary is writting with Go langage, you will use tools which are made for it.
you can typerabin2 -hto get help
Get rabin2 help
rabin2 -h
Usage: rabin2 [-AcdeEghHiIjJlLMqrRsSUvVxzZ] [-@ at] [-a arch] [-b bits] [-B addr]
[-C F:C:D] [-f str] [-m addr] [-n str] [-N m:M] [-P[-P] pdb]
[-o str] [-O help] [-k query] [-D lang mangledsymbol] file
-@ [addr] show section, symbol or import at addr
-A list sub-binaries and their arch-bits pairs
-a [arch] set arch (x86, arm, .. or <arch>_<bits>)
-b [bits] set bits (32, 64 ...)
-B [addr] override base address (pie bins)
-c list classes
-cc list classes in header format
-C [fmt:C:D] create [elf,mach0,pe] with Code and Data hexpairs (see -a)
-d show debug/dwarf information
-D lang name demangle symbol name (-D all for bin.demangle=true)
-e program entrypoint
-ee constructor/destructor entrypoints
-E globally exportable symbols
-f [str] select sub-bin named str
-F [binfmt] force to use that bin plugin (ignore header check)
-g same as -SMZIHVResizcld -SS -SSS -ee (show all info)
-G [addr] load address . address to header
-h this help message
-H header fields
-i imports (symbols imported from libraries)
-I binary info
-j output in json
-J ([var]) display variable
-k [sdb-query] run sdb query. for example: '*'
-K [algo] calculate checksums (md5, sha1, ..)
-l linked libraries
-L [plugin] list supported bin plugins or plugin details
-m [addr] show source line at addr
-M main (show address of main symbol)
-n [str] show section, symbol or import named str
-N [min:max] force min:max number of chars per string (see -z and -zz)
-o [str] output file/folder for write operations (out by default)
I usualy use -I options to know about the file
Get informations about the file
$rabin2 -I /bin/ls
arch x86
baddr 0x0
binsz 149359
bintype elf
bits 64
canary true
injprot false
class ELF64
crypto false
endian little
havecode true
intrp /lib64/ld-linux-x86-64.so.2
laddr 0x0
lang c
linenum false
lsyms false
machine AMD x86-64 architecture
nx true
os linux
pic true
relocs false
relro partial
rpath NONE
sanitize false
static false
stripped true
subsys linux
va true
Get imported symbols (libc functions, other shared objecs functions, class,..)
$rabin2 -i /bin/ls
nth vaddr bind type lib name
―――――――――――――――――――――――――――――――――――――
1 0x00004030 GLOBAL FUNC __ctype_toupper_loc
2 0x00004040 GLOBAL FUNC getenv
3 0x00004050 GLOBAL FUNC fgetfilecon
4 0x00004060 GLOBAL FUNC sigprocmask
5 0x00004070 GLOBAL FUNC __snprintf_chk
6 0x00004080 GLOBAL FUNC raise
7 ---------- GLOBAL FUNC __libc_start_main
8 0x00004090 GLOBAL FUNC abort
9 0x000040a0 GLOBAL FUNC __errno_location
10 0x000040b0 GLOBAL FUNC strncmp
11 ---------- WEAK NOTYPE _ITM_deregisterTMCloneTable
12 0x000040c0 GLOBAL FUNC _exit
13 0x000040d0 GLOBAL FUNC strcpy
14 0x000040e0 GLOBAL FUNC __fpending
15 0x000040f0 GLOBAL FUNC isatty
16 0x00004100 GLOBAL FUNC sigaction
17 0x00004110 GLOBAL FUNC iswcntrl
18 0x00004120 GLOBAL FUNC reallocarray
19 0x00004130 GLOBAL FUNC wcswidth
20 0x00004140 GLOBAL FUNC localeconv
21 0x00004150 GLOBAL FUNC faccessat
22 0x00004160 GLOBAL FUNC mbstowcs
23 0x00004170 GLOBAL FUNC readlink
24 0x00004180 GLOBAL FUNC clock_gettime
25 0x00004190 GLOBAL FUNC setenv
26 0x000041a0 GLOBAL FUNC textdomain
27 0x000041b0 GLOBAL FUNC fclose
28 0x000041c0 GLOBAL FUNC opendir
29 0x000041d0 GLOBAL FUNC getpwuid
30 0x000041e0 GLOBAL FUNC bindtextdomain
31 0x000041f0 GLOBAL FUNC dcgettext
32 0x00004200 GLOBAL FUNC __ctype_get_mb_cur_max
33 0x00004210 GLOBAL FUNC strlen
Get readable string from the file
you can do it with rabin2 like strings command (useful)
$rabin2 -z /bin/ls
nth paddr vaddr len size section type string
―――――――――――――――――――――――――――――――――――――――――――――――――――――――
0 0x0001a650 0x0001a650 11 12 .rodata ascii dev_ino_pop
1 0x0001a6c8 0x0001a6c8 10 11 .rodata ascii sort_files
2 0x0001a6d3 0x0001a6d3 6 7 .rodata ascii posix-
3 0x0001a6da 0x0001a6da 4 5 .rodata ascii main
4 0x0001a790 0x0001a790 10 11 .rodata ascii ?pcdb-lswd
5 0x0001a7a0 0x0001a7a0 65 66 .rodata ascii # Configuration file for dircolors, a utility to help you set the
6 0x0001a7e2 0x0001a7e2 72 73 .rodata ascii # LS_COLORS environment variable used by GNU ls with the --color option.
7 0x0001a82b 0x0001a82b 56 57 .rodata ascii # Copyright (C) 1996-2022 Free Software Foundation, Inc.
8 0x0001a864 0x0001a864 70 71 .rodata ascii # Copying and distribution of this file, with or without modification,
9 0x0001a8ab 0x0001a8ab 76 77 .rodata ascii # are permitted provided the copyright notice and this notice are preserved.
10 0x0001a8f8 0x0001a8f8 59 60 .rodata ascii # The keywords COLOR, OPTIONS, and EIGHTBIT (honored by the
11 0x0001a934 0x0001a934 61 62 .rodata ascii # slackware version of dircolors) are recognized but ignored.
12 0x0001a972 0x0001a972 73 74 .rodata ascii # Global config options can be specified before TERM or COLORTERM entries
13 0x0001a9bc 0x0001a9bc 72 73 .rodata ascii # Below are TERM or COLORTERM entries, which can be glob patterns, which
14 0x0001aa05 0x0001aa05 75 76 .rodata ascii # restrict following config to systems with matching environment variables.
15 0x0001aa51 0x0001aa51 12 13 .rodata ascii COLORTERM ?*
16 0x0001aa5e 0x0001aa5e 10 11 .rodata ascii TERM Eterm
17 0x0001aa69 0x0001aa69 9 10 .rodata ascii TERM ansi
18 0x0001aa73 0x0001aa73 12 13 .rodata ascii TERM *color*
19 0x0001aa80 0x0001aa80 21 22 .rodata ascii TERM con[0-9]*x[0-9]*
...
So in which case to use rabin2
Considere rabin2 as binary informations recon tool. You must use it a the biggening of your reverse project to gather a lot of informations about the binary file
- rasm2 (radare2 framework assembler and disassembler tool)
rasm2is a util for disassemble and assemble instruction.
It can be very useful for:
.shellecode scrafting
. shelllecode disassembled
. assembled langage training
It support a lot of architectures and many options
Get rasm2 help
$rasm2 -h
Usage: rasm2 [-ACdDehHLBvw] [-a arch] [-b bits] [-s addr] [-S syntax]
[-f file] [-o file] [-F fil:ter] [-i skip] [-l len] 'code'|hex|0101b|-
-a [arch] set architecture to assemble/disassemble (see -L)
-A show Analysis information from given hexpairs
-b [bits] set cpu register size (8, 16, 32, 64) (RASM2_BITS)
-B binary input/output (-l is mandatory for binary input)
-c [cpu] select specific CPU (depends on arch)
-C output in C format
-d, -D disassemble from hexpair bytes (-D show hexpairs)
-e use big endian instead of little endian
-E display ESIL expression (same input as in -d)
-f [file] read data from file
-F [parser] specify which parse filter use (see -LL)
-h, -hh show this help, -hh for long
-H ([var]) display variable
-i [len] ignore/skip N bytes of the input buffer
-j output in json format
-k [kernel] select operating system (linux, windows, darwin, android, ios, ..)
-l [len] input/Output length
-L ([name]) list RArch plugins: (a=asm, d=disasm, e=esil)
-LL ([name]) list RAsm parse plugins
-N same as r2 -N (or R2_NOPLUGINS) (not load any plugin)
-o [file] output file name (rasm2 -Bf a.asm -o a)
-p run SPP over input for assembly
-q quiet mode
-r output in radare commands
-s,-@ [addr] define initial start/seek address (default 0)<br>
-S [syntax] select syntax (intel, att)<br>
-v show version information<br>
-x use hex dwords instead of hex pairs when assembling.>br>
-w what's this instruction for? describe opcode <br>
If '-l' value is greater than output length, output is padded with nops
If the last argument is '-' reads from stdin
Environment:<br>
Get a list of supported arch
$rasm2 -L
_de 8 6502 Disassembler for the 6502 microprocessor family (NES, c64, ..)
_de 8 6502.cs Capstone mos65xx 8 bit microprocessors
ade 8 16 8051 8051 microcontroller (also known as MCS-51)
_de 64 alpha ALPHA architecture disassembler based on GNU binutils
_de 32 amd29k AMD 29k decoder
a__ 16 32 64 any.as Use system's gnu/clang 'as' assembler
a__ 8 16 32 64 any.vasm Use asm.cpu=6502, 6809, c16x, jagrisc, m68k, pdp11, ppc,qnice, tr3200, vidcore, x86, z80
_de 16 32 arc ARC processor instruction decoder
a__ 16 32 64 arm.nz Custom thumb, arm32 and arm64 assembler
_de 16 32 64 arm Capstone ARM analyzer
_de 16 32 64 arm.gnu ARM code analysis plugin (asm.cpu=wd for winedbg disassembler)
ade 8 16 avr AVR microcontroller CPU by Atmel
ade 32 bf brainfuck architecture
ade 32 bpf.mr BPF the Berkeley Packet Filter bytecode
_de 32 64 bpf Capstone BPF bytecode
_de 32 chip8 CHIP8 virtual CPU architecture
_de 8 16 cosmac RCA COSMAC MicroProcessor 180X family
_de 16 cr16 Compact RISC processor
_de 32 cris Axis Communications 32-bit embedded processor
_de 32 dalvik Dalvik (Android VM) bytecode
_de 32 dis Inferno Dis VM disassembler
_de 32 64 ebc EFI Bytecode architecture
ade 32 evm EthereumVM bytecode (EVM)
_de 32 fslsp Freescale QorIQ service processor
ade 16 gb Gameboy CPU analysis (modified Z80)
_de 8 16 h8300 H8300 High Speed 8-bit cpu with internal 16 bit architecture
_de 16 hppa HP PA-RISC
ade 4 i4004 The classic Intel 4004
_de 16 i8080 Intel 8080 CPU
ade 32 java Java bytecode
_de 16 jdh8 JDK-8 toy architecture
_de 64 kvx Kalray VLIW core
_de 32 lanai Myricom s LANAI based on GNU binutils
_de 8 lh5801 SHARP LH5801 microprocessor
_de 32 lm32 Lattice Micro 32 ISA
Disassemble hex string (maybe consolecode in hex version)
$rasm2 -d "9090905050"
nop
nop
nop
push rax
push rax
Assembled instruction
rasm2 -a x86 "nop; nop; nop; push rax; push rax"
9090905050
- rax2 a convertor
rax2 is a calculotor/convertor for difference base.
With it, you :
. make some compute
. convert betwen base hex to string for example
…
Rax2 help
$rax2 -h
Usage: rax2 [-h|...] [- | expr ...] # convert between numeric bases
int -> hex ; rax2 10
hex -> int ; rax2 0xa
-int -> hex ; rax2 -77
-hex -> int ; rax2 0xffffffb3
int -> bin ; rax2 b30
int -> ternary ; rax2 t42
bin -> int ; rax2 1010d
ternary -> int ; rax2 1010dt
float -> hex ; rax2 3.33f
hex -> float ; rax2 Fx40551ed8
oct -> hex ; rax2 35o
hex -> oct ; rax2 Ox12 (O is a letter)
bin -> hex ; rax2 1100011b
hex -> bin ; rax2 Bx63
ternary -> hex ; rax2 212t
hex -> ternary ; rax2 Tx23
raw -> hex ; rax2 -S < /binfile
hex -> raw ; rax2 -s 414141
-a show ascii table ; rax2 -a
-b <base> output in <base> ; rax2 -b 10 0x46
-c output in C string ; rax2 -c 0x1234 # \x34\x12\x00\x00
-C dump as C byte array ; rax2 -C < bytes
-d force integer ; rax2 -d 3 -> 3 instead of 0x3
-e swap endianness ; rax2 -e 0x33
-D base64 decode ; rax2 -D "aGVsbG8="
-E base64 encode ; rax2 -E "hello"
-f floating point ; rax2 -f 6.3+2.1
-F stdin slurp code hex ; rax2 -F < consolecode.[c/py/js]
-h help ; rax2 -h
-H hash string ; rax2 -H linux osx
-i IP address <-> LONG ; rax2 -i 3530468537
-j json format output ; rax2 -j 0x1234 # same as r2 -c '?j 0x1234'
-k keep base ; rax2 -k 33+3 -> 36
-K randomart ; rax2 -K 0x34 1020304050
Apart those mantioned utilities, whe have other:
- rarun2
used to run binary in customise environment - rahash2
binary hashing, hashing comparaison , … util - radiff2
diffind finder. useful to compare difference version of the same software to found the difference - rafind2:
find pattern on the binary - R2pipe
which is a plugin to integrate radare2 on multiple langage like python, C++. this help to write reverse engineering script
Refere to the help part for more usage
Binary open modes
So let start your reverse engineering journee with radare2.
Open binary for static and dynamic analyse
With radare2, we have multiple mode in which you can open the binary:
. Read Only mode
Considere the case where you don’t want to patch the binary. You only want to make static anlyse.
Type this to open /bin/ls in read-only mode
radare2 /bin/ls
you will get a console where you start inspecting things, disassemble function and so one
$radare2 /bin/ls
WARN: Relocs has not been applied. Please use `-e bin.relocs.apply=true` or `-e bin.cache=true` next time
-- Check your IO plugins with 'r2 -L'
[0x000061d0]>
- Read-Write mode
You open the binary in Read - Write when you plan to make some modification of it. Patch the binary for example.
To do that, you must specifi the -w option on radare2 commande.
Make sure that you have write permission on the file. see bellow
└──╼ $radare2 -w ./ls
WARN: Relocs has not been applied. Please use `-e bin.relocs.apply=true` or `-e bin.cache=true` next time
-- Invert the block bytes using the 'I' key in visual mode
[0x000061d0]>
That give you a console on which you analyse and modify the binary file
When you are on read only mode, you reopen the binary by typing oo+
- Debug mode
The debug mode is very useful to debug the program (make breakpoints and other)
To open the file in debug mode, use -d option. See bellow ``` $radare2 -dw ./ls – To debug a program, you can call r2 with ‘dbg://' or '-d ' [0x7fa438c98b20]>
``` Nice so you get a console to debug the program and make dynamic analyse
Interfaces
When you open a binary file with radare2, you get a console. That shell is the main interface of the tool. You can do a lot of thing inside it.
With it, we also have others interfaces:
. Visual mode:
To inter in visual mode :
type V on the console
The visual mode help you swhitching between other mode like hexeditor mode, disassemble mode, …
Once you are one visual mode, you can use p to swhich between others mode.
You can also use HJKL touch to navigate (like vim editor) on visual mode
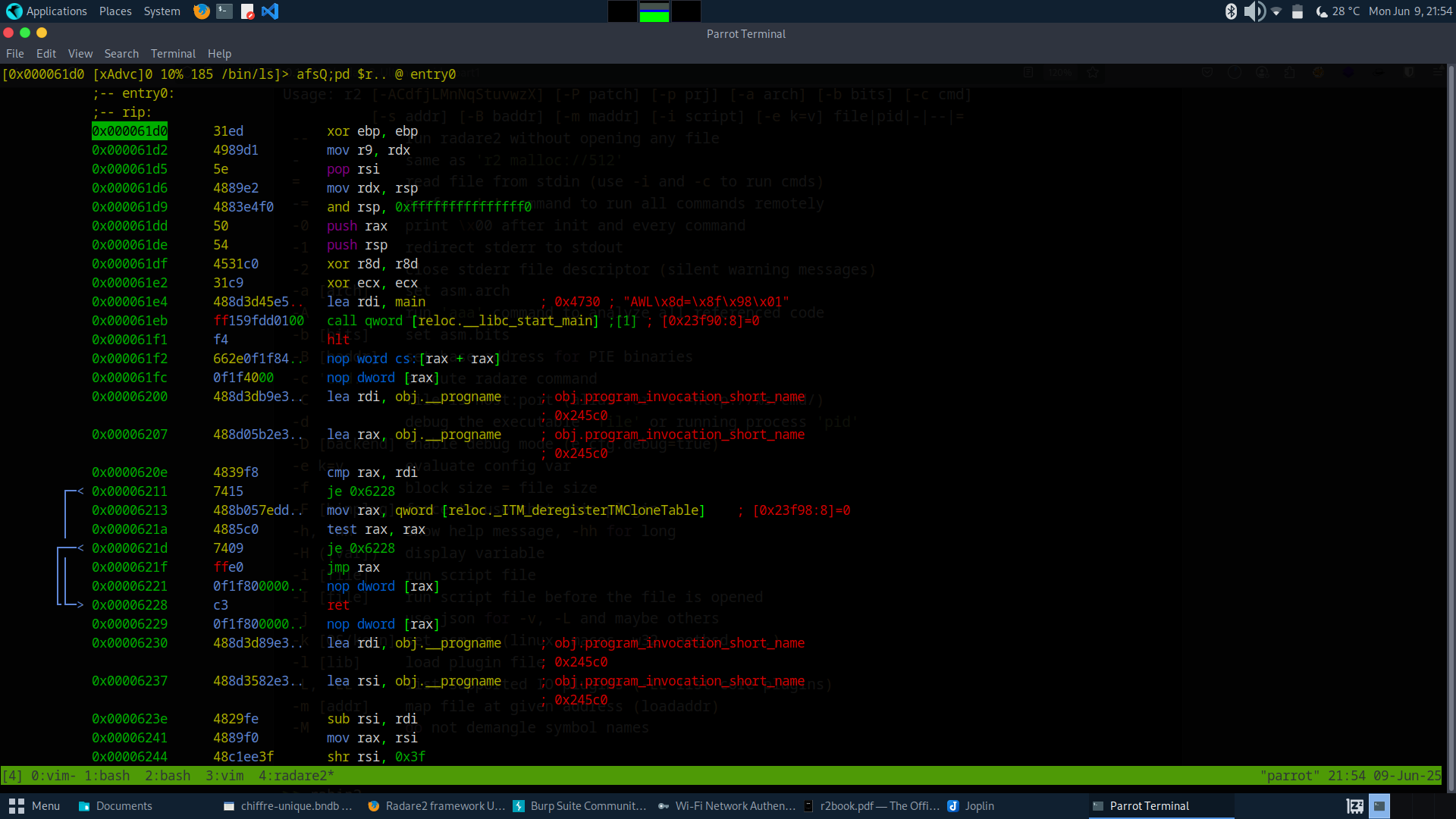
Visual: disassembled mode
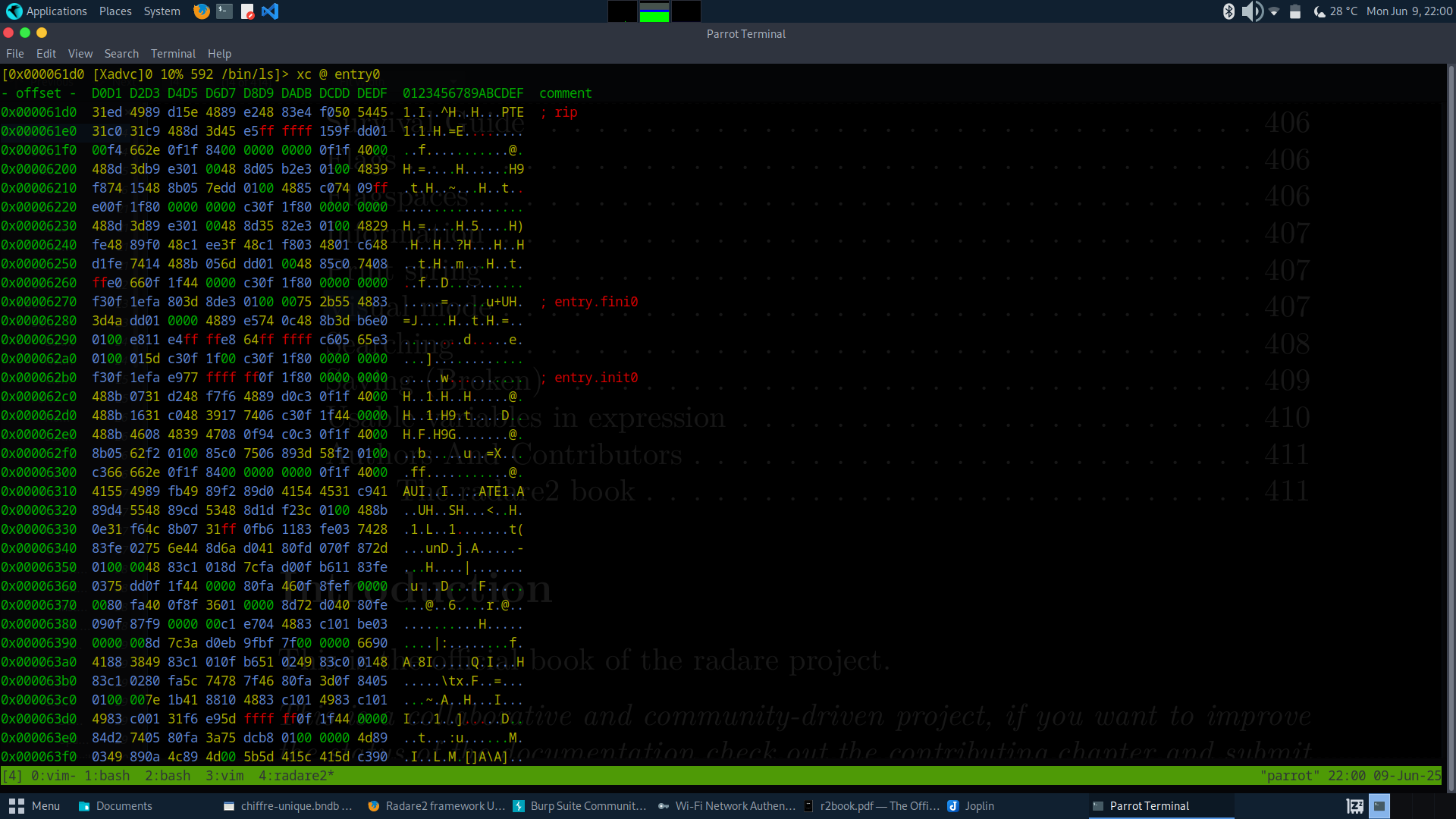
Visual: Hex editor mode
To quit Visual mode, type q
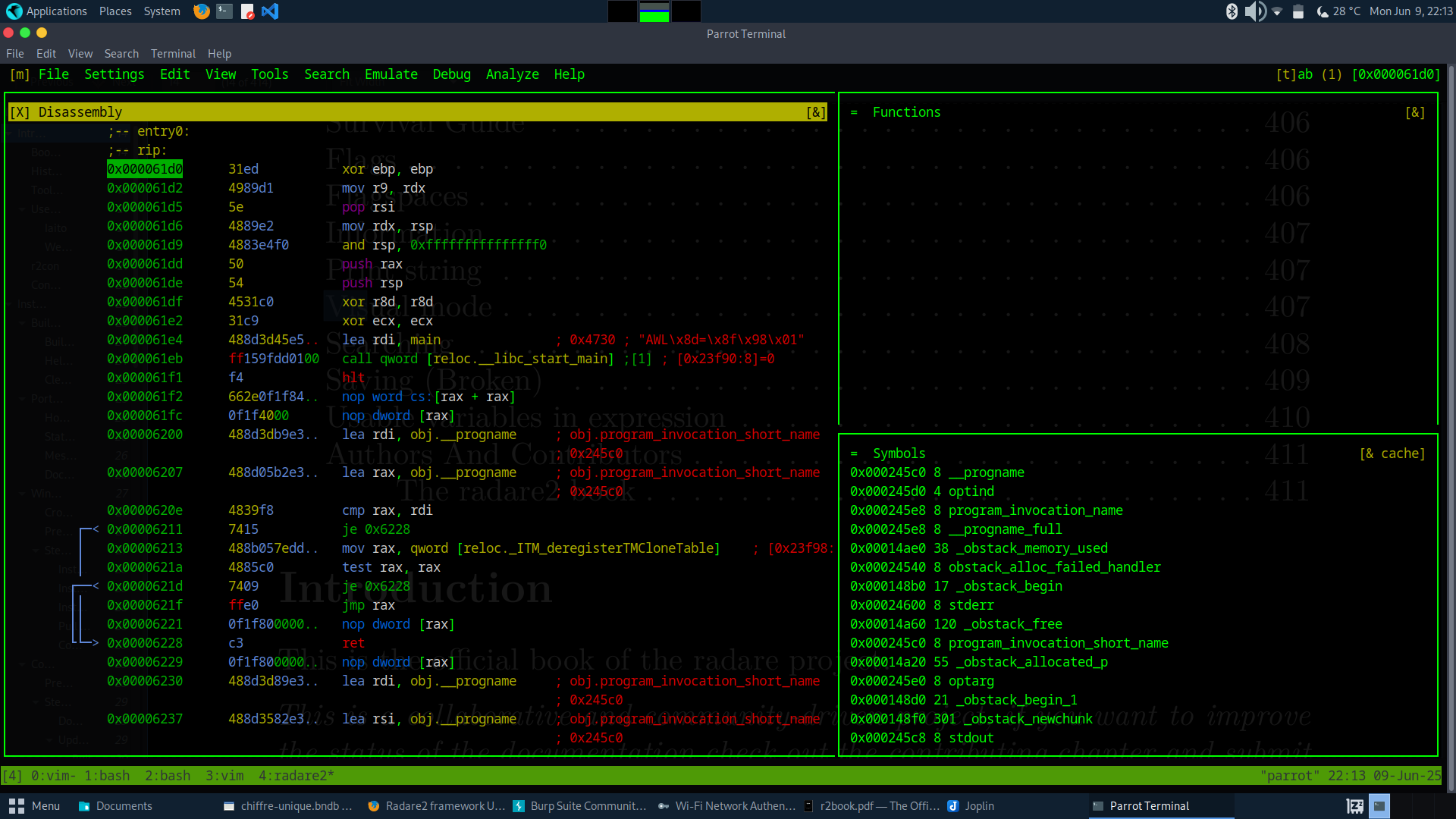
- Graphi mode or visual panel
Even if radare2 is commande line tool, it offer graphic mode Which still is a console interface. A graphic mode divide your terminal into many parts:
. Disassembled code part
. Functions part
. Graph . Comment . Symbol part
….
****************************** radare2 GRAPIC MODE ************
Thing about Ghidra graphic intercace
On graphic mode, You can use your mouse. to do thing like:
. open/close the file
. Open/close/save project: we will talk about project on other chapter
. Acess to setting
. Change setting
You can also customise this graphic interface
. tab to swhitch betwen panel
. m to access toolbar options
. . x to close the actual selected panel
. | vertical selected layout
. - horizontal selected layout
. w modify the width
. ? get help( useful)
. enter to zoom the selected layout
. YOU can also customize layout and save it for the next.
to do that: m, swhitch to setting, layou,save layout or load layout
End
This article was an overview of radare2 framework .
In the next article , we can start effectively use radare2. We will learn radare2 commands and also do some static/dynamic analyse with it.
Hope you learn something from this article !!!! Enjoy.
It was @Top0n3 the Planet Hacker :-)